Definitions and Abbreviations
This section is details all the definitions and abbreviations needed for your P1 - Private Pilot License.
All of the definitions and abbreviations below are referenced from the General Authority of Civil Aviation - GACA.
GACA Part 001 Definitions and Abbreviations
Definitions
ACAS I
An ACAS which provides information as an aid to “see and avoid” action but does not include the capability for generating resolution advisories (RAs).
ACAS II
An ACAS which provides vertical resolution advisories (RAs) in addition to traffic advisories (TAs).
ACAS III
An ACAS which provides vertical and horizontal resolution advisories (RAs) in addition to traffic advisories (TAs).
Acrobatic flight
Maneuvers intentionally performed by an aircraft involving an abrupt change in its attitude, an abnormal attitude, or an abnormal variation in speed.
Advanced aircraft
An aircraft with equipment in addition to that required for a basic aircraft for a given take-off, approach or landing operation.
Advisory airspace
An airspace of defined dimensions, or designated route, within which air traffic advisory service is available.
Aerodrome
A defined area on land or water (including any buildings, installations and equipment) intended to be used either wholly or in part for the arrival, departure and surface movement of aircraft.
Aerodrome control tower
A unit established to provide air traffic control service to aerodrome traffic.
Aerodrome elevation
The elevation of the highest point of the landing area.
Aerodrome traffic
All traffic on the maneuvering area of an aerodrome and all aircraft flying in the vicinity of an aerodrome. Note— An aircraft is in the vicinity of an aerodrome when it is in, entering or leaving an aerodrome traffic circuit.
Aerodrome traffic zone
An airspace of defined dimensions established around an aerodrome for the protection of aerodrome traffic.
Aeronautical chart
A representation of a portion of the Earth, its culture and relief, specifically designated to meet the requirements of air navigation.
Aeronautical Information Publication (AIP)
A publication issued by or with the authority of a State and containing aeronautical information of a lasting character essential to air navigation.
Aeroplane
A power-driven heavier-than-air aircraft, deriving its lift in flight chiefly from aerodynamic reactions on surfaces which remain fixed under given conditions of flight. Note — Also referred to as "airplane".
Air defense identification zone (ADIZ)
Special designated airspace of defined dimensions within which aircraft are required to comply with special identification and/or reporting procedures additional to those related to the provision of air traffic services.
Air traffic
All aircraft in flight or operating on the maneuvering area of an aerodrome.
Air traffic control clearance
Authorization for an aircraft to proceed under conditions specified by an air traffic control unit. Note 1— For convenience, the term “air traffic control clearance” is frequently abbreviated to “clearance” when used in appropriate contexts. Note 2— The abbreviated term “clearance” may be prefixed by the words “taxi,” “take-off,” “departure,” “en route,” “approach" or “Landing" to indicate the particular portion of flight to which the air traffic control clearance relates.
Air traffic control service
A service provided for the purpose of:
Air traffic control unit
A generic term meaning variously, area control center, approatch control unit or aerodrome control tower.
Air traffic service (ATS)
A generic term meaning variously, flight information service, alerting service, air traffic advisory service, air traffic control service (area control service, approach control service or aerodrome control service).
Air traffic services airspaces
Airspaces of defined dimensions, alphabetically designated, within which specific types of flights may operate and for which air traffic services and rules of operation are specified. Note— ATS airspaces are classified as Class A to G.
AIRAC
An acronym (aeronautical information regulation and control) signifying a system aimed at advance notification, based on common effective dates, of circumstances that necessitate significant changes in operating practices.
Aircraft
Any machine that can derive support in the atmosphere from the reactions of the air other than the reactions of the air against the earth’s surface.
Aircraft — category
Classification of aircraft according to specified basic characteristics, e.g. airplane, helicopter, glider, free balloon.
Aircraft — type
Aircraft type of All aircraft of the same basic design including all modifications thereto except those modifications which result in a change in handling or flight characteristics.
Aircraft avionics
A term designating any electronic device — including its electrical part — for use in an aircraft, including radio, automatic flight control and instrument systems. Note— Also referred to as "Avionics"
Aircraft certificated for single-pilot operation
A type of aircraft which the State of Registry has determined, during the certification process, can be operated safely with a minimum crew of one pilot.
Aircraft equipment
Articles, including first-aid and survival equipment and commissary supplies, but not spare parts or stores, for use on board an aircraft during flight.
Aircraft operating manual
A manual, acceptable to the State of the Operator, containing normal, abnormal and emergency procedures, checklists, limitations, performance information, details of the aircraft systems and other material relevant to the operation of the aircraft. Note — The aircraft operating manual is part of the operations manual.
Aircraft operator
A person, organization or enterprise engaged in or offering to engage in an aircraft operation.
Airframe The fuselage, booms, nacelles, cowlings, fairings, airfoil surfaces (including rotors but excluding propellers and rotating engine airfoils), and landing gear of an aircraft and their accessories and controls.
Airman
A person holding, or required to hold, a current and valid certificate or authorization issued under GACAR Part 61, 64, 65 or66.
Airmanship
The consistent use of good judgement and well-developed knowledge, skills and attitudes to accomplish flight objectives.
Airship
A power-driven lighter-than-air aircraft.
Airway
A control area or portion thereof established in the form of a corridor.
Airworthiness certificate
A document issued by a state certifying that an aircraft complies with the design aspects of appropriate airworthiness requirements. Note— Also referred to as “Certificate of Airworthiness”.
Airworthiness directive (AD)
A legally enforceable rule that applies to aircraft registered in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. ADs are designed to be applicable to specific types of aircraft or engines, propellers, and articles that are part of the aircraft type design, even if an individual product or article has been changed by modifying, altering, or repairing it in the area addressed by an airworthiness directive.
Airworthy
The status of an aircraft, engine, propeller or part when it conforms to its approved design and is in a condition for safe operation.
Altitude
The vertical distance of a level, a point or an object considered as a point, measured from mean sea level.
Apron
A defined area, on a land aerodrome, intended to accommodate aircraft for purposes of loading or unloading passengers, mail or cargo, fueling, parking or maintenance.
ASHTAM
A special series NOTAM notifying by means of a specific format change in activity of a volcano, a volcanic eruption and/or volcanic ash cloud that is of significance to aircraft operations.
Automatic dependent surveillance-Broadcast (ADS-B)
A means by which aircraft, aerodrome vehicles and other objects can automatically transmit and/or receive data such as identification, position and additional data, as appropriate, in a broadcast mode via a data link. ADS-B OUT: A function on an aircraft or vehicle that periodically broadcasts its state vector (position and velocity) and other information derived from on-board systems in a format suitable for ADS-B IN capablere ceivers. ADS-B IN: A function that receives surveillance data from ADS-B OUT data sources.
Automatic terminal information service
The automatic provision of current, routine information to arriving and departing aircraft throughout 24 hours or a specified portion thereof: Data link-automatic terminal information service (D-ATIS). The provision of ATIS via data link. Voice-automatic terminal information service (Voice-ATIS). The provision of ATIS by means of continuous and repetitive voice broadcasts.
Blind transmission
A transmission from one station to another station in circumstances where two-way communication cannot be established but where it is believed that the called station is able to receive the transmission.
Broadcast
A transmission of information relating to air navigation that is not addressed to a specific station or stations.
Cargo aircraft
Any aircraft, other than a passenger aircraft, which is carrying goods or property.
Ceiling
The height above the ground or water of the base of the lowest layer of cloud below 6 000 metres (20 000 feet) covering more than half the sky.
Class
-
As used with respect to the certification, ratings, privileges, and limitations of airmen, means a classification of aircraft within a category having similar operating characteristics. Examples include: single engine, multiengine, land, water, gyroplane, helicopter, airship, and free balloon; and
-
As used with respect to the certification of aircraft, means a broad grouping of aircraft having similar characteristics of propulsion, flight, or landing. Examples include: airplane, rotorcraft, glider, balloon, landplane, and seaplane.
Clearway
A defined rectangular area on the ground or water under the control of the appropriate authority, selected or prepared as a suitable area over which an airplane may make a portion of its initial climb to a specified height.
Complex airplane
An airplane that has a retractable landing gear, flaps, and a controllable pitch propeller, including airplanes equipped with an engine control system consisting of a digital computer and associated accessories for controlling the engine and propeller, such as a full authority digital engine control; or, in the case of a seaplane, flaps and a controllable pitch propeller, including seaplanes equipped with an engine control system consisting of a digital computer and associated accessories for controlling the engine and propeller, such as a full authority digital engine control.
Congested area
In relation to a city, town or settlement, any area which is substantially used for residential, commercial or recreational purposes.
Control area (CTA)
A controlled airspace extending upwards from a specified limit above the earth.
Control zone
A controlled airspace extending upwards from the surface of the earth to a specified upper limit.
Controlled aerodrome
An aerodrome at which air traffic control service is provided to aerodrome traffic. Note— The term “controlled aerodrome” indicates that air traffic control service is provided to aerodrome traffic but does not necessarily imply that a control zone exists.
Controlled airspace
An airspace of defined dimensions within which air traffic control service is provided in accordance with the airspace classification. Note— Controlled airspace is a generic term which covers ATS airspace classes A, B, C, D and E.
Controlled flight
Any flight which is subject to an air traffic control clearance.
Controller-pilot data link communications (CPDLC)
A means of communication between controller and pilot, using data link for ATC communications.
Cross-country
A flight between a point of departure and a point of arrival following a pre-planned route using standard navigation procedures.
Danger area
An airspace of defined dimensions within which activities dangerous to the flight of aircraft may exist at specified times.
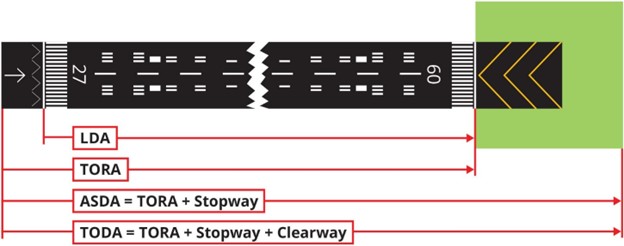
Declared distances:
-
Take-off run available (TORA). The length of runway declared available and suitable for the ground run of an airplane takingoff.
-
Take-off distance available (TODA). The length of the take-off run available plus the length of the clearway, if provided.
-
Accelerate-stop distance available (ASDA). The length of the take-off run available plus the length of the stopway, if provided.
-
Landing distance available (LDA). The length of runway which is declared available and suitable for the ground run of an airplane landing.
Displaced threshold
A threshold not located at the extremity of a runway.
Ditching
The forced landing of an aircraft on water.
Emergency locator transmitter (ELT)
A generic term describing equipment which broadcast distinctive signals on designated frequencies and, depending on application, may be automatically activated by impact or be manually activated.
Estimated time of arrival
For VFR flights, the time at which it is estimated that the aircraft will arrive over the aerodrome.
Filed flight plan
The flight plan as filed with an ATS unit by the pilot or a designated representative, without any subsequent changes.
Flight information region (FIR)
An airspace of defined dimensions within which flight information service and alerting service are provided.
Flight manual
A manual, associated with the certificate of airworthiness, containing limitations within which the aircraft is to be considered airworthy, and instructions and information necessary to the flight crew members for the safe operation of the aircraft.
Flight plan
Specified information provided to air traffic services units, relative to an intended flight or portion of a flight of an aircraft.
GACA
The General Authority of Civil Aviation.
High-performance airplane
An airplane with an engine capable of producing more than 150 kW.
Isogonal
A line on a map or chart on which all points have the same magnetic variation for a specified epoch.
Knot (kt)
The speed equal to 1 nautical mile per hour.
Landing area
That part of a movement area intended for the landing or take-off of aircraft.
Large airplane
An airplane of a maximum certificated take-off mass of over 5 700 kg.
Magnetic Bearing
The horizontal direction to or from any point, usually measured clockwise from true north, magnetic north, or some other reference point through 360 degrees.
Magnetic variation
The angular difference between True North and Magnetic North. Note— The value given indicates whether the angular difference is East or West of True North.
Maneuvering area
That part of an aerodrome to be used for the take-off, landing and taxiing of aircraft, excluding aprons.
Nautical mile (NM)
The length equal to 1 852 meters exactly.
Night
The hours between the end of evening civil twilight and the beginning of morning civil twilight or such other period between sunset and sunrise, as may be prescribed by the appropriate authority. Note— Civil twilight ends in the evening when the center of the sun’s disc is 6 degrees below the horizon and begins in the morning when the center of the sun’s disc is 6 degrees below the horizon.
NOTAM
A notice distributed by means of telecommunication containing information concerning the establishment, condition or change in any aeronautical facility, service, procedure or hazard, the timely knowledge of which is essential to personnel concerned with flight operations.
Pilotage
Navigation by visual reference to landmarks.
Prohibited area
An airspace of defined dimensions, above the land areas or territorial waters of a State, within which the flight of aircraft is prohibited.
Radial
A magnetic bearing extending from a VOR/VORTAC/TACAN.
Rating
An authorization entered on or associated with a license and forming part thereof, stating special conditions, privileges or limitations pertaining to such license.
Readback
A procedure whereby the receiving station repeats a received message or an appropriate part thereof back to the transmitting station so as to obtain confirmation of correct reception.
Runway
A defined rectangular area on a land aerodrome prepared for the landing and take-off of aircraft.
Runway incursion
Any occurrence at an aerodrome involving the incorrect presence of an aircraft, vehicle or person on the protected area of a surface designated for the landing and take-off of aircraft.
Runway-holding position
A designated position intended to protect a runway, an obstacle limitation surface, or an ILS/MLS critical/sensitive area at which taxiing aircraft and vehicles shall stop and hold, unless otherwise authorized by the aerodrome control tower.
Special VFR flight
A VFR flight cleared by air traffic control to operate within a control zone in meteorological conditions below VMC.
Surveillance radar
Radar equipment used to determine the position of an aircraft in range and azimuth.
Taxiing
Movement of an aircraft on the surface of an aerodrome under its own power, excluding take-off and landing.
Taxiway
A defined path on a land aerodrome established for the taxiing of aircraft and intended to provide a link between one part of the aerodrome and another.
Terminal control area
A control area normally established at the confluence of ATS routes in the vicinity of one or more major aerodromes.
Threshold
The beginning of that portion of the runway usable for landing.
Touchdown
The point where the nominal glide path intercepts the runway.
Touchdown zone
The portion of a runway, beyond the threshold, where it is intended landing airplanes first contact the
Track
The projection on the earth’s surface of the path of an aircraft, the direction of which path at any point is usually expressed in degrees from North (true, magnetic or grid).
Traffic pattern
the traffic flow that is prescribed for aircraft landing at, taxiing on, or taking off from, an airport.
Vectoring
Provision of navigational guidance to aircraft in the form of specific headings, based on the use of an ATS surveillance system.
Visibility
Visibility for aeronautical purposes is the greater of:
-
the greatest distance at which a black object of suitable dimensions, situated near the ground, can be seen and recognized when observed against a bright background;
-
the greatest distance at which lights in the vicinity of 1 000 candelas can be seen and identified against an unlit background.
Abbreviations
| Abbreviations | Definitions |
|---|
| ACAS | Airborne collision avoidance system |
| ADS-B | Automatic dependent surveillance broadcast |
| AFIS | Aerodrome flight information service |
| AFM | Aircraft flight manual |
| AGL | Above ground level |
| AIP | Aeronautical information publication |
| AME | Aviation medical examiner |
| AOC | Air operator certificate |
| ATIS | Automatic terminal information service |
| ATS | Air traffic services |
| CAS | Calibrated airspeed |
| CFIT | Controlled flight into terrain |
| DME | Distance measuring equipment |
| EFIS | Electronic flight instrument system |
| ELT | Emergency locator transmitter |
| FIR | Flight information region |
| FSTD | Flight simulation training device |
| GACA | The General Authority of Civil Aviation |
| GPS | Global positioning system |
| IAS | Indicated airspeed |
| IFR | Instrument flight rules |
| IMC | Instrument meteorological conditions |
| MSL | Mean sea level |
| NOTAM | Notice to Airmen |
| PAPI | Precision approach path indicator |
| PIC | Pilot in command |
| RVR | Runway visual range |
| SIC | Second in command |
| SMS | Safety management system |
| SSR | Secondary surveillance radar |
| TAS | True airspeed |
| TCAS | Traffic alert and collision avoidance system |
| TIBA | Traffic information broadcast by aircraft |
| V1 | Takeoff decision speed |
| V2 | Takeoff safety speed |
| VA | Designed maneuvering speed |
| VF | Design flap speed |
| VFE | Maximum flap extended speed |
| VFR | Visual flight rules |
| VHF | Very high frequency |
| VMC | Visual metrological condition |
| VMO / MMO | Maximum operating limit speed |
| VNE | Never exceed speed |
| VNO | Maximum structural cruising speed |
| VR | Rotation speed |
| VREF | Reference landing speed |
| VS | The stalling speed or the minimum steady flight speed at which the airplane is controllable |
| VS0 | The stalling speed or the minimum steady flight speed in the landing configuration |
| VX | Speed for the best angle of climb |
| VY | Speed for the best rate of climb |
